What is HIV?
HIV, or the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a virus that weakens the immune system over time. It damages the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases, leading to the progression to AIDS if untreated. HIV is primarily transmitted through certain body fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
Risk Factors for HIV Infection
The risk factors for HIV infection include:
- Engaging in unprotected sexual activities with multiple partners or with someone whose HIV status is unknown.
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- Receiving blood transfusions, organ transplants, or other medical procedures with contaminated equipment.
- Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
Early Symptoms of HIV
Early symptoms of HIV, which may appear 2-4 weeks post-infection, include:
- Fever and Fatigue: A flu-like illness with fever and general tiredness.
- Rash: A rash that can cover various parts of the body.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged glands in the neck, armpits, or groin.
- Sore Throat and Mouth Sores: Painful swallowing and ulcers in the mouth.
- Headaches and Muscle Pain: Persistent headaches and muscle aches throughout the body.
HIV Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Medications
HIV PEP involves taking antiretroviral medications to reduce the risk of HIV infection after potential exposure. The specific medications include:
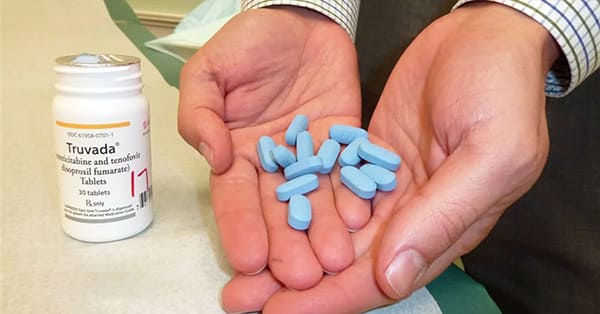
- Truvada: A fixed-dose combination of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, which is often the first line of defense in PEP. It works by blocking the activity of the virus and preventing it from multiplying in the body.
- Other medications may include tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), emtricitabine (FTC), dolutegravir (DTG), and raltegravir (RAL), which may be used in combination with Truvada or as part of a PEP regimen.
The Principle of HIV Preventing
The principle of HIV blocking is based on the rapid initiation of antiretroviral therapy post-exposure to prevent the virus from establishing a long-term infection. By inhibiting key enzymes, these medications prevent the virus from replicating and integrating into the host's DNA.
The Use of HIV Blocking Medications
PEP should be started as soon as possible after potential exposure to HIV, ideally within 72 hours. The medications are typically taken for a 28-day period and must be taken consistently and as prescribed to be effective.
Access to HIV Blocking Medications
Access to HIV PEP medications can be obtained through various avenues:
- Healthcare Providers: Consultation with a healthcare provider for a prescription and guidance.
- Emergency Departments: Some hospitals' emergency departments may offer PEP after-hours.
- Specialized Clinics: HIV treatment centers and infectious disease clinics often stock these medications.
- Online Services: In some regions, telemedicine consultations can provide prescriptions for PEP.
- Pharmacies: With a valid prescription, medications can be dispensed at local pharmacies.
Conclusion
HIV PEP is a crucial preventive measure for individuals who have been potentially exposed to the virus. Understanding the symptoms, recognizing the risk factors, and knowing the available medications, especially the role of Truvada in PEP, are vital steps towards preventing the spread of HIV. Immediate action and access to healthcare are key to the success of PEP in reducing the risk of HIV infection.